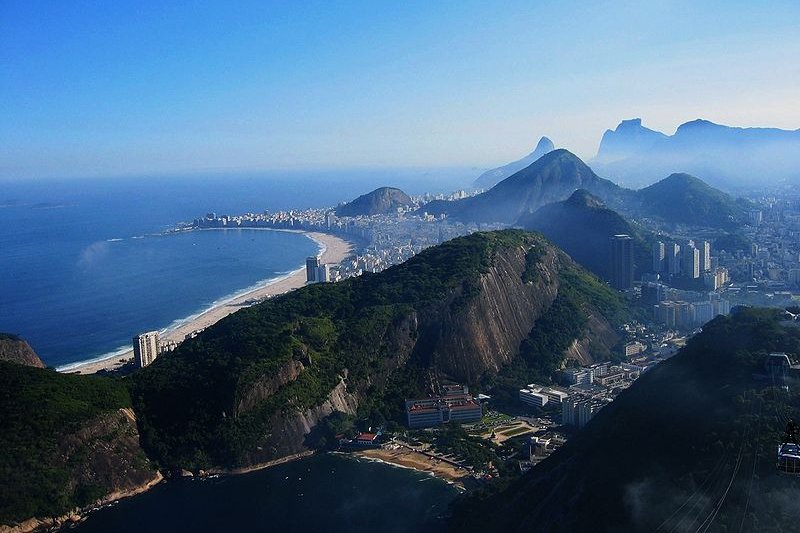
 A scenic aerial view of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
A scenic aerial view of Rio de Janeiro, BrazilSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Rio_de_Janeiro_from_Sugarloaf_mountain,_May_2004.jpg
Author: Breogan67

Brazil is the largest country in South America and the fifth largest in the world. It covers 8,514,877 sq km (3,287,597 sq mi) of the eastern part of the South American continent, and has a population of 191 million (2011 estimate). The capital of Brazil is Brasilia while the largest city is São Paulo.
Brazil is the only Portuguese-speaking country in the Americas as well as the most populous Portuguese-speaking country in the world. It shares a border with almost all the countries of South America including, in counter-clockwise direction, French Guiana, Suriname, Guyana, Venezuela, Colombia, Peru, Bolivia, Paraguay, Argentina and Uruguay. Also within Brazilian territory are numerous archipelagos in the South Atlantic Ocean. The only South American countries not having a shared border with Brazil are Ecuador and Chile.
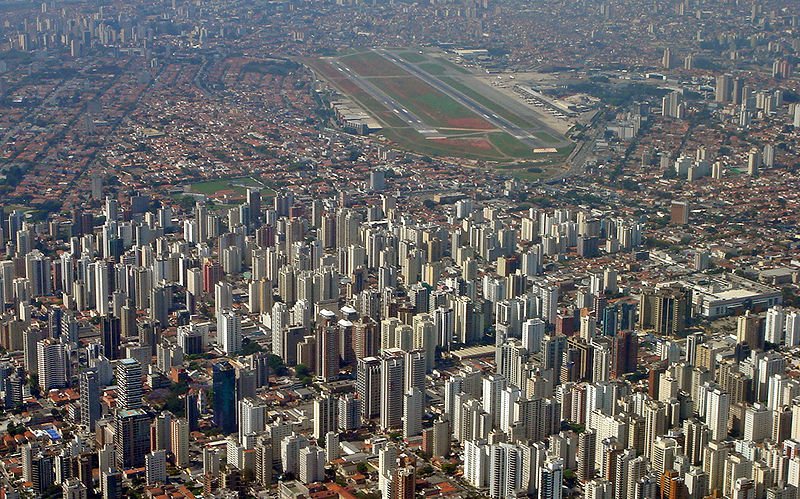 São Paulo skyscrapers
São Paulo skyscrapersSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Sao_Paulo_Congonhas_2.jpg
Author: Mariordo

Due to the large expanse of the country, Brazil has three time zones namely Brasilia Official Time (3 hours behind Coordinated Universal Time) observed by Brasilia and the big cities of southeastern Brazil; Brasilia Time + 1 (UTC-02) observed by a few Atlantic islands on the east coast of Brasil; and Brasilia Tim - 1 (UTC-04) observed by states of Amazonas, Mato Grosso, Mato Grosso do Sul, Rondônia and Roraima.
In Brazil, vehicles drive on the right side. The phone IDD code is +55. The official currency is the Real (R$). Brazil in 2010 has a nominal GDP of $2.023 trillion, equivalent to a per capita nominal GDP of $10,471. The per capita GDP at purchasing power parity is $11,289.
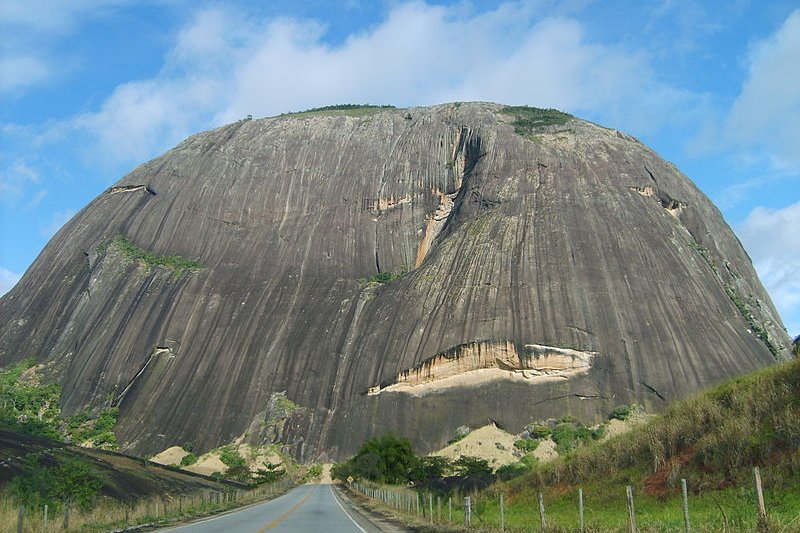 Mountain in Mato Grosso
Mountain in Mato GrossoSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Mountains_in_MG.JPG
Author: Jacson

History of Brazil
Brazil was claimed by Portuguese explorer Pedro Álvares Cabral for Portugal in April 1500. The land was already inhabited by a number of primitive tribes who are often at war with one another. The natives speak a tongue of the Tupi-Guarani linguistic family.Although Brazil was a colony of Portugal since 1500, the first settlement was only established in 1532. The early years of contact with the natives brought wars, diseases, extermination and enslavement which decimated the indigenous tribes. Throughout the 16th century, the Portuguese continued to expand their territorial coverage of Brazil, ousting the French, the British and the Dutch from their respective outposts.
In 1808 the Portuguese royal family, in fleeing advancing troops of Napoleon Bonaparte, reestablished themselves in Rio de Janeiro, making it the seat of the Portuguese Empire. In 1815, the regent Dom João VI elevated Brazil to Kingdom united with Portugal.
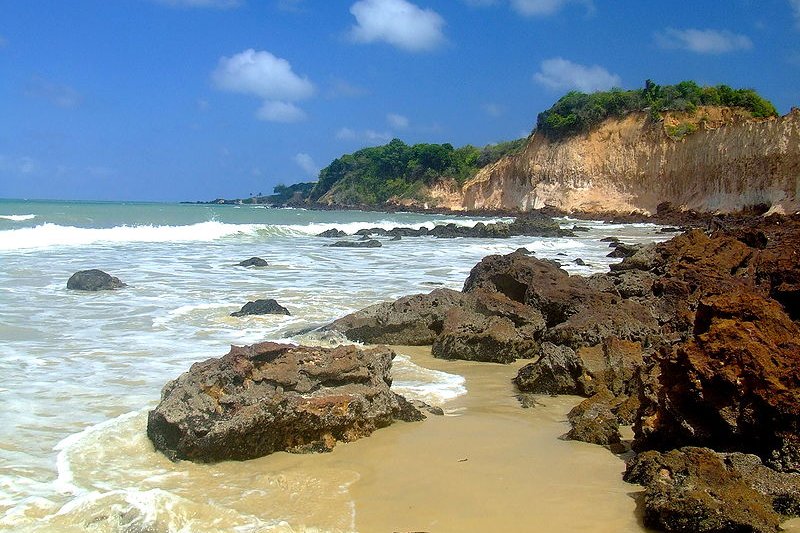 Praia de Cotovelo, Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil
Praia de Cotovelo, Rio Grande do Norte, BrazilSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Praia_de_Cotovelo_-_Parnamirim_-_Rio_Grande_do_Norte.jpg
Author: Fábio Pinheiro
When King João VI returned to Europe on 26 April, 1821, he left his eldest son Prince Pedro de Alcântara behind as regent to rule Brazil. The Portuguese attempted to return Brazil to colonial status again, but the Brazilians refused. Prince Pedro supported the movement for Brazilian independence, and was later crowned the Emperor of Brazil on 1 December, 1822.
The Brazilian monarchy was overthrown on 15 November 1889, despite the emperor being at the height of its popularity. The coup was backed by slave owners who opposed the abolition of slavery brought on in 1888. A military dictatorship took over the government, and the country was plagued by a series of rebellions, civil unrest and revolt. In 1930, the defeated presidential candidate Getúlio Vargas even successfully led a coup d'état and took over presidency.
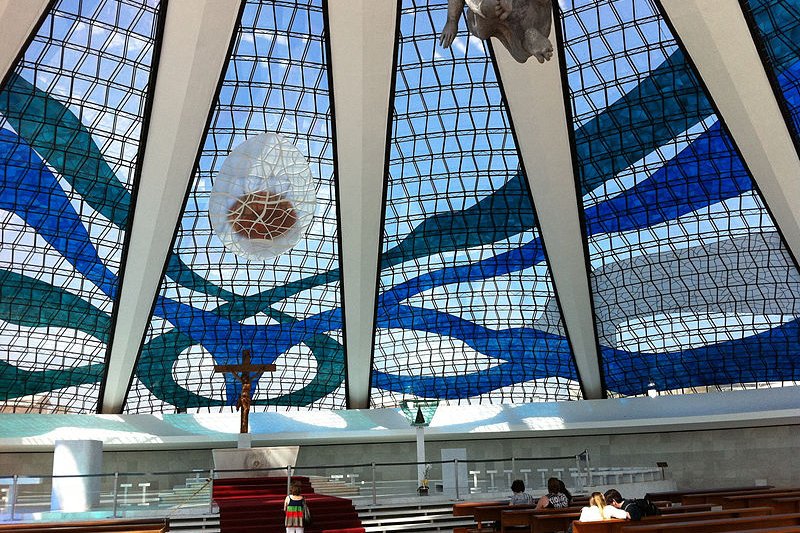 Catedral de Brasilia
Catedral de BrasiliaSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Inside_the_Catedral_de_Bras%C3%ADlia.jpg
Author: anna carol
The new capital city of Brasilia was inaugurated in 1960. Through much of the 20th century, the political landscape of Brasil was tumultuous. A military dictatorship ruled the country from 1964 until 1985, when José Sarney became president. However the unsuccessful civilian government of José Sarney is remembered for unbridled inflation and severe economic crisis.
Long term stability only came about for Brazil when Fernando Henrique Cardoso was appointed Minister of Finance. As architect of the Plano Real (Royal Plan), he brought stability to the Brazilian economy. Cardoso was elected president in 1994, and again in 1998. The presidency has since transitioned peacefully to Luís Inácio Lula da Silva in 2002, re-elected in 2006, and succeeded in 2011 by current president Dilma Rousseff.
Planning your trip to Brazil
The São Paulo-Guarulhos International Airport (GRU) is the biggest airport in Brazil with numerous direct flights with major cities in North America and Europe. The second biggest airport is the Rio de Janeiro-Galeão International Airport (GIG). Both airports offer good connections with cities throughout Brazil.Preparing Money for your trip to Brazil
The currency used in Brazil is the Brazilian Real (BRL). Major Cities in Brazil
Major Cities in Brazil
- Brasília - capital
- São Paulo - biggest city
- Belo Horizonte
- Florianópolis
- Fortaleza
- Manaus
- Porto Alegre
- Recife
- Rio de Janeiro
- Salvador
 World Heritage Sites in Brazil
World Heritage Sites in Brazil
Brazil ratified the World Heritage Convention on 1 September, 1977. As of August 2010, it has 10 Cultural World Heritage Sites and 7 Natural World Heritage Sites. Brazil has also submitted another 17 sites for consideration, presently on the World Heritage Tentative List.Brazil has served on the World Heritage Committee for four mandates, 1980-1987, 1987-1993, 1993-1999 and 2007-2011.
-
Cultural
- Historic Town of Ouro Preto (1980)
- Historic Centre of the Town of Olinda (1982)
- Jesuit Missions of the Guaranis: São Miguel das Missoes (1983)
- Historic Centre of Salvador de Bahia (1985)
- Sanctuary of Bom Jesus do Congonhas (1985)
- Brasilia (1987)
- Serra da Capivara National Park (1991)
- Historic Centre of São Luís (1997)
- Historic Centre of the Town of Diamantina (1999)
- Historic Centre of the Town of Goiás (2001)
- São Francisco Square in the Town of São Cristovão (2010)
- Rio de Janeiro: Carioca Landscapes between the Mountain and the Sea (2012)
- Iguaçu National Park (1986)
- Atlantic Forest South-East Reserves (1999)
- Discovery Coast Atlantic Forest Reserves (1999)
- Central Amazon Conservation Complex (2000)
- Pantanal Conservation Area (2000)
- Brazilian Atlantic Islands: Fernando de Noronha and Atol das Rocas Reserves (2001)
- Cerrado Protected Areas: Chapada dos Veadeiros and Emas National Parks (2001)
Natural
- Les Couvents Franciscains du Nord-Est Brésilien (1996)
- Ensemble architectonique de tourisme et loisir au bord du lac de Pampulha (1996)
- Eglise et Monast`re de Sao Bento, Rio de Janeiro (1996)
- Palais de la Culture, ancien siège du Ministère de l'Education et de la Santé, Rio de Janeiro (1996)
- Parc national du Pico da Neblina (Amazonas) (1996)
- Parc national de la Serra da Bocaina (São Paulo - Rio de Janeiro) (1996)
- Réserve biologique d'Atol das Rocas (Rio Grande do Norte) (1996)
- Station écologique de Taim (Rio Grande do Sul) (1996)
- Station écologique du Raso da Catarina (Bahia) (1996)
- Canyon du Rio Peruaçu, Minas Gerais (1998)
- Anavilhanas Ecological Station (1998)
- Serra do Divisor National Park (1998)
- Serra da Canastra National Park (1998)
- Cavernas do Peruaçu Federal Environmental Protection Area (APA) / Veredas Do Peruaçu State Park (1998)
- Serra da Capivara National Park and Permanent Preservation Areas (1998)
- Rio de Janeiro Cultural Landscape (2001)
- Gold Route in Parati and its landscape (2004)
States of Brazil
-
Northern Region
- Acre
- Amapá
- Amazonas
- Pará
- Rondônia
- Roraima
- Tocantins
- Alagoas
- Bahia
- Ceará
- Maranhão
- Paraíba
- Pernambuco
- Piauí
- Rio Grande do Norte
- Sergipe
- Goiás
- Mato Grosso
- Mato Grosso do Sul
- Espirito Santo
- Minas Gerais
- Rio de Janeiro
- São Paulo
- Rio Grande do Sul
- Paraná
- Santa Catarina
Major Attractions of Brazil
- Chapada dos Veadeiros
- Christ the Redeemer Statue
- Iguaçu Falls
- Itaipu Dam
- Itatiaia National Park
- Pantanal
 Latest updates on Penang Travel Tips
Latest updates on Penang Travel Tips

Copyright © 2003-2025 Timothy Tye. All Rights Reserved.

 Go Back
Go Back