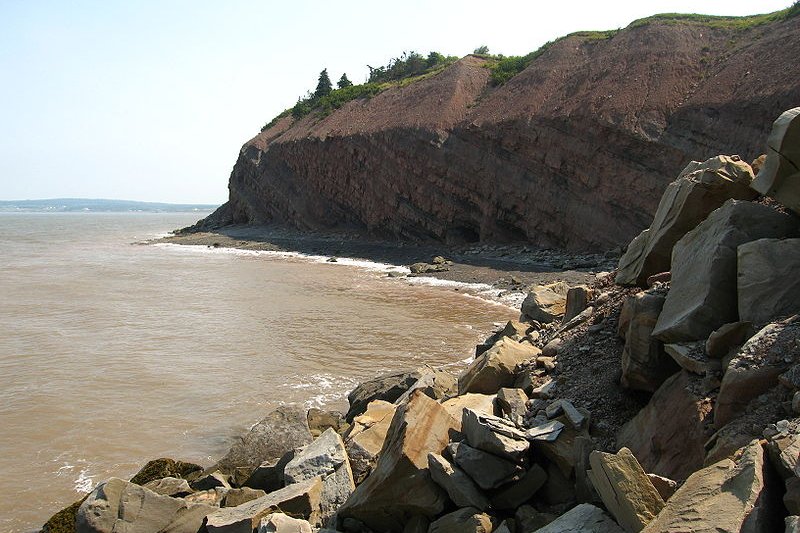
 Joggins Fossil Cliffs
Joggins Fossil CliffsSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Joggins_Fossil_Cliffs_on_the_Bay_of_Fundy_at_Joggins,_NS_-_08734.JPG
Author: Dustin M. Ramsey
Joggins Fossil Cliffs are an important paleontological site along the coast of Nova Scotia in eastern Canada. The cliffs have been nicknamed the "coal age Galápagos" due to their wealth of fossils from the Carboniferous Period, which is 354 to 290 million years ago. The rocks in Joggins Fossil Cliffs are significant to the study of the history of the earth, as they are the world's thickest and most comprehensive record of the Pennsylvanian strata, which dates from 318 to 303 million years ago. Within these rocks are some of the most complete fossil records of terrestrial lifeform from that age.
Visitors to Joggins Fossil Cliffs can see the remains and footprints of early animals, still intact and undisturbed. The site span a distance of 14.7 kilometers, and includes sea cliffs, low bluffs, rock platforms and beach. Together, they showcase three different ecosystems, namely estuarine bay, floodplain rainforest and fire prone forest alluvial plain with freshwater pools. Joggins Fossil Cliffs are the richest assemblage of fossil life from these three ecosystems. So far, 96 genera and 148 species of fossils have been studied, along with 20 footprint groups. The site was inscribed as a World Heritage Site during the 32nd session of the World Heritage Committee meeting in Quebec City, Canada on 2-10 July, 2008.
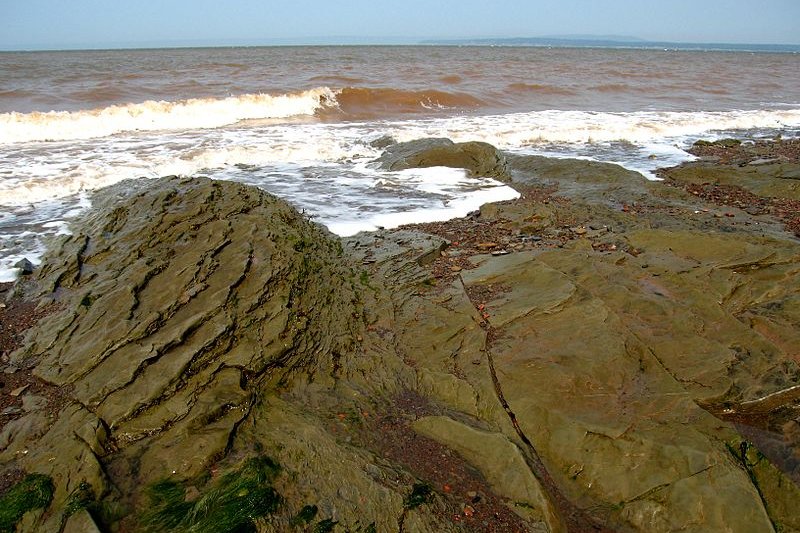 Chignecto Bay, Joggins Fossil Cliffs, Nova Scotia
Chignecto Bay, Joggins Fossil Cliffs, Nova ScotiaSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Chignecto_Bay_and_Cape_Chignecto_on_the_Bay_of_Fundy_at_Joggins,_NS_-_08724.JPG
Author: Dustin M. Ramsey
Joggins was formerly a coal mining area. Coal mining had been carried out here since 1686 by local Acadian settlers, who are descendants of 17th century French colonists. The first commercial coal mine was established here in 1731, but was destroyed by the Mi'kmaq native American tribe the following year.
Coal mining continued to be carried out at Joggins right through the 20th century, when the coal was also used to feed two electrical generating stations. The last mine only closed following the Springhill Mining Disaster of 1958.
World Heritage Site Inscription Details
Location: N 45 42 35 W 64 26 9 in Nova Scotia, CanadaInscription Year: 2008
Type of Site: Natural
Inscription Criteria: VIII
Visiting Joggins Fossil Cliffs
You can go there by flight to Halifax, Nova Scotia, or to Moncton, New Brunswick. From either airports, I suggest you rent a car. From Halifax, take Highway 102 North, followed by Provincial Route 102 North for 74 km. Then take Trans Canada Highway West for 98 km. Continue on Highway 2 and take exit 4 towards Amherst/Springhill/South Albion Street. Turn left onto Albion Street. Then continue on Provincial Secondary Route 2 for 2.5 km. Then turn right onto Highway 302, pass through Nappan. Turn right onto Highway 242, travel 13 km passing through River Herbert, then another 5km up Main Street to Joggins. Latest updates on Penang Travel Tips
Latest updates on Penang Travel Tips

Copyright © 2003-2025 Timothy Tye. All Rights Reserved.

 Go Back
Go Back