The Royal Observatory is part of the Maritime Greenwich World Heritage Site.
The Royal Observatory, Greenwich (formerly the Royal Greenwich Observatory or RGO) was commissioned in 1675 by King Charles II. The king also created the position of Astronomer Royal, with John Flamsteed being the first to occupy the position, as the director of the observatory and to "apply himself with the most exact care and diligence to the rectifying of the tables of the motions of the heavens, and the places of the fixed stars, so as to find out the so much desired longitude of places for the perfecting of the art of navigation." The Royal Observatory, Greenwich, is situated on a hill in Greenwich Park in Greenwich, London, overlooking the River Thames.
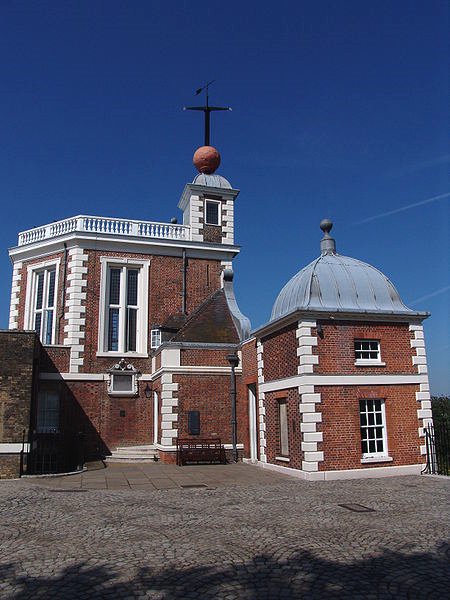 Royal Observatory Greenwich
Royal Observatory GreenwichSource: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Greenwich-Royal_Observatory-016.jpg
Author: Tilman2007
Until 1954, Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) was based on the time observations made at Greenwich. After that, GMT was calculated from observations made at other observatories which were still active. Today GMT is often called Universal Time, because it is now calculated from observations of extra-galactic radio sources and then converted. To help others synchronize their clocks to GMT, a time ball was installed by Astronomer Royal John Pond in 1833. It still drops daily to mark the exact moment of 1 p.m. (13:00) year round (GMT during winter and BST during summer).
The difference between Royal Observatory, Greenwich and Royal Greenwich Observatory
For much of the 20th century, the Royal Greenwich Observatory was not at Greenwich. The last time all the departments were there was in 1924: the arrival of the railway that year affected the readings of the Magnetic And Meteorological Department and forced it to move out, to Abinger. Many departments were also evacuated in 1939, on the on set of World War II to the countryside, to places such as Abinger, Bradford, and Bath, and activities in Greenwich were reduced to the bare minimum.
After the War, the Royal Greenwich Observatory departments were moved to Herstmonceux Castle, about 70 km south-southeast of Greenwich in East Sussex, to avoid the pollution in London. The scientific staff moved there upon the completion of the new observatory buildings in 1957. The Isaac Newton Telescope was built in Herstmonceux in 1967. However, it was then moved to Roque de los Muchachos Observatory in the Canary Islands in 1979. In 1990, the Royal Greenwich Observatory moved again, to Cambridge. When it closed in 1998, Her Majesty's Nautical Almanac Office moved into the Rutherford Appleton Laboratory while other departments went to the UK Astronomy Technology Centre in Edinburgh. Herstmonceux Castle now houses the International Study Centre of Queen's University, Kingston, Canada and the Observatory Science Centre.
Today the Royal Observatory buildings include a museum of astronomical and navigational tools, which is part of the National Maritime Museum, and John Harrison's prize-winning longitude marine chronometer, among others. It is also home to the 28-inch Grubb refracting telescope, the largest telescope of its kind in the UK.
In February 2005 construction work began on a £15 million redevelopment project. It was completed on 25 May, 2007, to add the 120 seat Peter Harrison Planetarium and additional display galleries and educational facilities to the Royal Observatory.
List of Historical buildings in London

Copyright © 2003-2025 Timothy Tye. All Rights Reserved.

 Royal Observatory, Greenwich, London
Royal Observatory, Greenwich, London Go Back
Go Back